As the automotive industry transitions towards electric vehicles (EVs), the demand for public charging infrastructure is growing rapidly. While the focus on electric passenger cars has been prevalent, the electrification of vans and light commercial vehicles (LCVs) is gaining momentum, presenting a unique set of challenges and opportunities for public charging infrastructure.
Challenges and Barriers
The electrification of vans and LCVs presents a significant challenge for public charging infrastructure due to the vehicles’ higher power requirements and longer charging times compared to passenger cars. Additionally, LCVs often operate on longer routes and have more demanding duty cycles, requiring a more robust and widespread charging network.
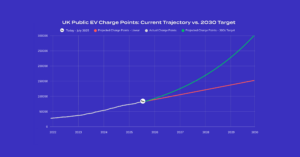
One of the most pressing issues is the uneven distribution of public charging points. While urban areas are generally better served, rural and suburban regions often lack adequate infrastructure, posing a significant barrier for fleets operating in these areas. This lack of accessibility can deter fleet operators from adopting electric vans and LCVs, hindering the overall adoption of EVs in the commercial sector.
Another challenge lies in the compatibility of charging connectors. Unlike passenger cars, which have largely standardized on the Combined Charging System (CCS), LCVs have a wider range of connectors, including CHAdeMO, Type 2, and Tesla’s proprietary connector. This diversity can complicate the development and deployment of standardized charging stations, making it difficult to cater to a diverse fleet of LCVs.
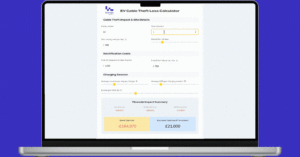
Furthermore, the cost of installing and maintaining public charging infrastructure is higher for vans and LCVs due to their higher power demands. This can be a deterrent for businesses considering investing in charging point infrastructure, especially in areas with lower usage rates.
Potential Solutions
To overcome these challenges and accelerate the adoption of electric vans and LCVs, a comprehensive approach to public charging infrastructure is essential. This includes:
- Strategic Planning and Collaboration: Coordinated planning between government agencies, industry bodies, and infrastructure providers is crucial to ensure a well-planned and integrated network of charging points across urban, suburban, and rural areas. Public-private partnerships can play a key role in funding and developing charging infrastructure.
- Standardization and Harmonization: Aligning on a single standard for charging connectors, such as CCS, can simplify the installation and operation of charging stations, making them more accessible to a wider range of LCVs. This standardization will also facilitate compatibility with the growing number of electric van models entering the market.
- Smart Charging Technologies: Implementing smart charging technologies can optimize the utilization of charging points, ensuring that vehicles are charged efficiently and minimizing congestion at popular locations. This includes dynamic load balancing, which manages the power draw from multiple vehicles, and predictive charging, which pre-plans charging sessions to avoid peak demand periods.
- Business Models and Incentives: Developing attractive business models for public charging providers can encourage investment and expansion. This could include tiered pricing structures based on usage, time of day, and vehicle type, as well as incentives for businesses and fleet operators to install charging points at their premises.
- Investments in Grid Infrastructure: Upgrading the electricity grid to handle the increased demand from electric vehicles is essential. This includes strengthening distribution networks, upgrading transformers, and investing in renewable energy sources to power the charging infrastructure.
The electrification of vans and LCVs presents a significant opportunity to reduce emissions and improve air quality in urban environments. However, achieving widespread adoption will require a concerted effort to address the challenges in public charging infrastructure. By implementing strategic planning, standardization, smart charging technologies, innovative business models, and grid infrastructure investments, we can pave the way for a future where electric vans and LCVs are seamlessly integrated into our transportation systems.